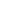Family Tree:
Dinosauria
Saurischia
Theropoda
Tetanurae
Carnosauria
Allosauroidea
Metriacanthosauridae
Dinosauria
Saurischia
Theropoda
Tetanurae
Carnosauria
Allosauroidea
Metriacanthosauridae
Pronunciation: sin-rap-toh-rUh-day
Author: Currie and Zhao
Year: 1994
Meaning: Chinese plunderers (see etymology)
Locomotion: Bipedal (two legs)
Senior Synonym: Metriacanthosauridae
Author: Currie and Zhao
Year: 1994
Meaning: Chinese plunderers (see etymology)
Locomotion: Bipedal (two legs)
Senior Synonym: Metriacanthosauridae
[Sereno, 2005]Definition
The most inclusive clade containing Sinraptor dongi but not Allosaurus fragilis, Carcharodontosaurus saharicus, and Passer domesticus (house sparrow).
About
After 18 relatively peaceful years as a valid family name, Sinraptoridae was trumped by Metriacanthosaurus, which was long considered a species of Megalosaurus and thus a member of Megalosauridae, and drew suspicious glances from palaeontologists, even after Grep Paul used it to anchor its own family, Metriacanthosauridae, in 1988. But when Carrano recovered Metriacanthosaurus as a member of Sinraptoridae in 2012, the laws of priority came into effect, and because Metriacanthosauridae was named before Sinraptoridae, the latter became a junior synonym of the former. That is not a bad thing, as the name Sinraptoridae (see etymology) suggests all "sinraptorids" were Chinese when, in fact, they are not.
Click here to search Dinochecker's database for Metriacanthosaurids.
Etymology
Sinraptoridae is derived from the Greek "sinai" (Chinese), the Latin "raptor" (plunderer), and the Greek "idae" (family), named for group anchor, Sinraptor.References
• Paul GS (1988) "Predatory Dinosaurs of the World". Simon &
Schuster, New York, 464 pp.
• Currie P J and Zhao X-J (1994) "A new carnosaur (Dinosauria, Theropoda) from the Jurassic of Xinjiang, People's Republic of China". Canadian Journal of Earth Sciences 30(10-11): 2037-2081.
• Carrano MT, Benson RBJ and Sampson SD (2012) "The phylogeny of Tetanurae (Dinosauria: Theropoda)". Journal of Systematic Palaeontology, 10(2): 211-300. DOI: 10.1080/14772019.2011.630927